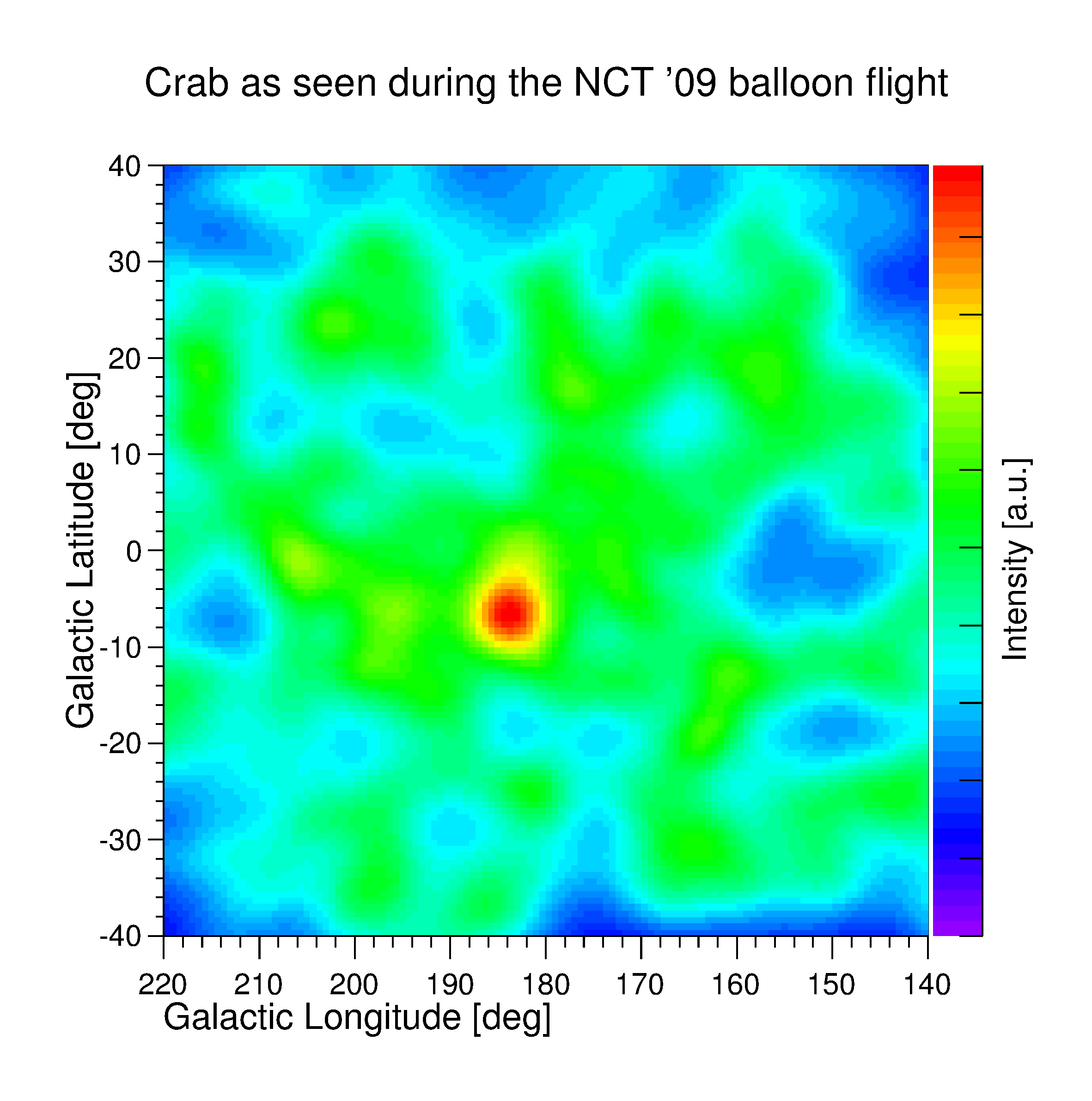
This image has been obtained with the data from the 2009 balloon campaign of the Nuclear Compton Telescope NCT . It uses the Compton event data obtained during the 7 hours at floating altitude of 40 km where Crab was in the field-of-view of NCT. The Crab (pulsar and nebula) is clearly visible as the only source with a detection significance of ~6 sigma. This image has been reconstructed using MEGAlib's Compton image reconstruction tool Mimrec.
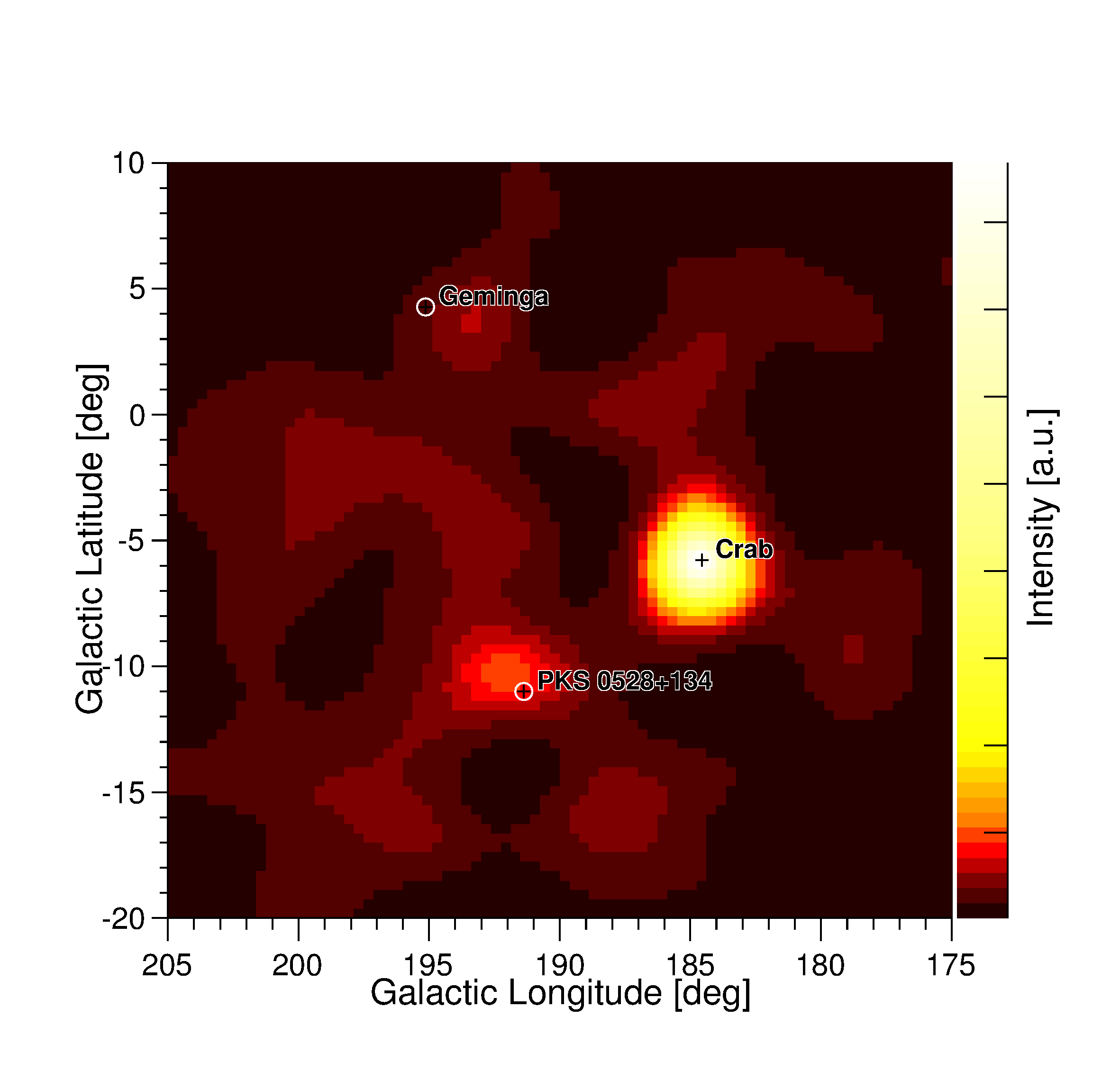
The Galactic anti-center region in the 30 to 50 MeV range as seen with COMPTEL. The Crab (pulsar + nebula) is the single detected source. An analysis in ARM space shows that the Crab has been detected with 6-7 sigma and its FWHM is 1.6 degrees.
This is the first image using COMPTEL data above 30 MeV. Using MEGAlib it was for the first time possible to extend COMPTEL's energy range above 30 MeV and to create an image of the Crab with Compton events.
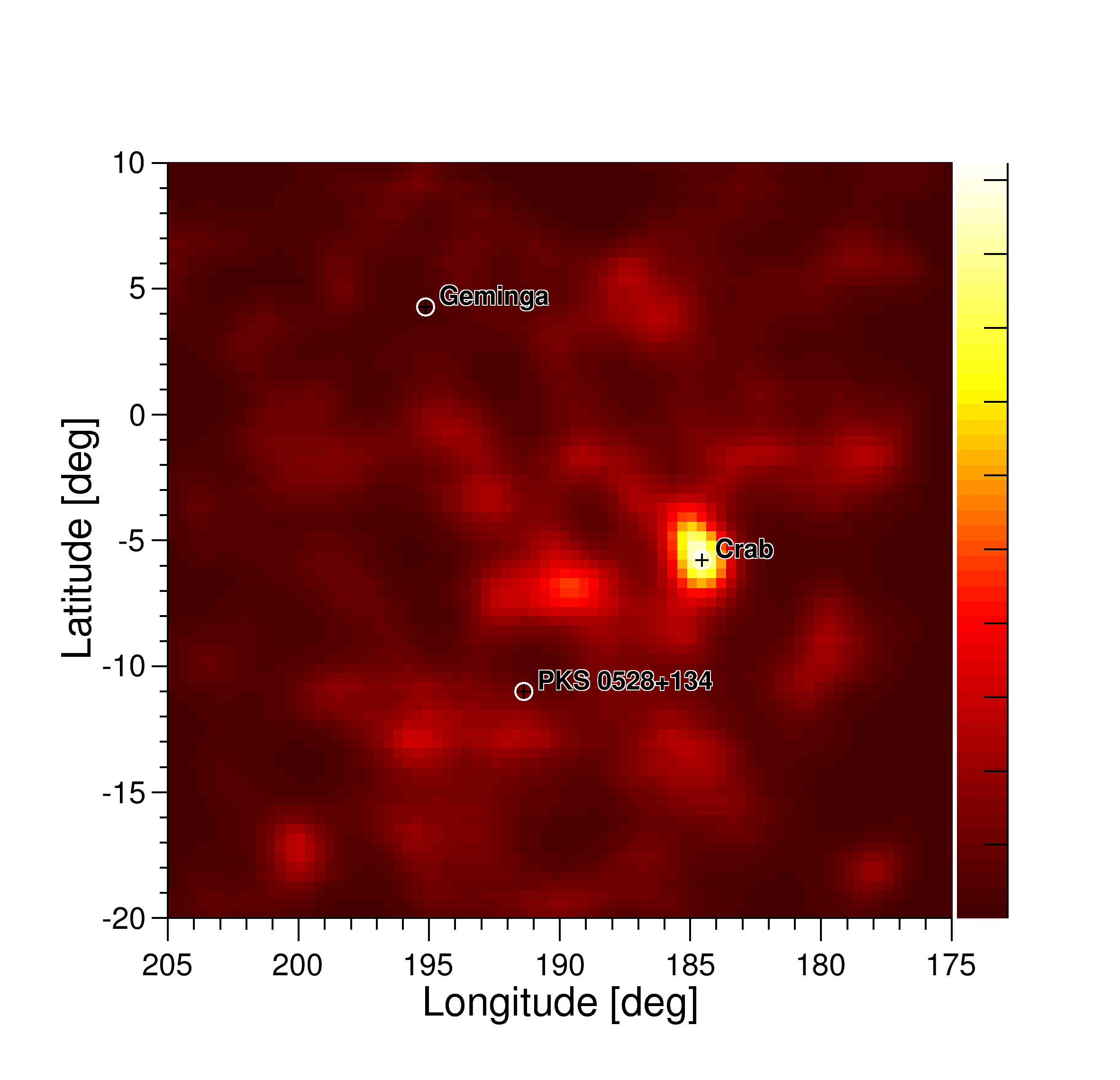
This image shows the Galactic anti-center as observed with COMPTEL in the energy range from 10 to 30 MeV. The Crab (nebula and pulsar - 69 sigma detection) is the dominating source. The second strongest source is PKS 0528+134 (~6 sigma detection), a highly variable blazar. The third-highest maximum is 2 degrees off the well known pulsar Geminga, which is a strong EGRET/FERMI source above 100 MeV, but which was not detected with the original COMPTEL analysis. However, it does not fulfill the requirements for a source detection, and thus might just be background.
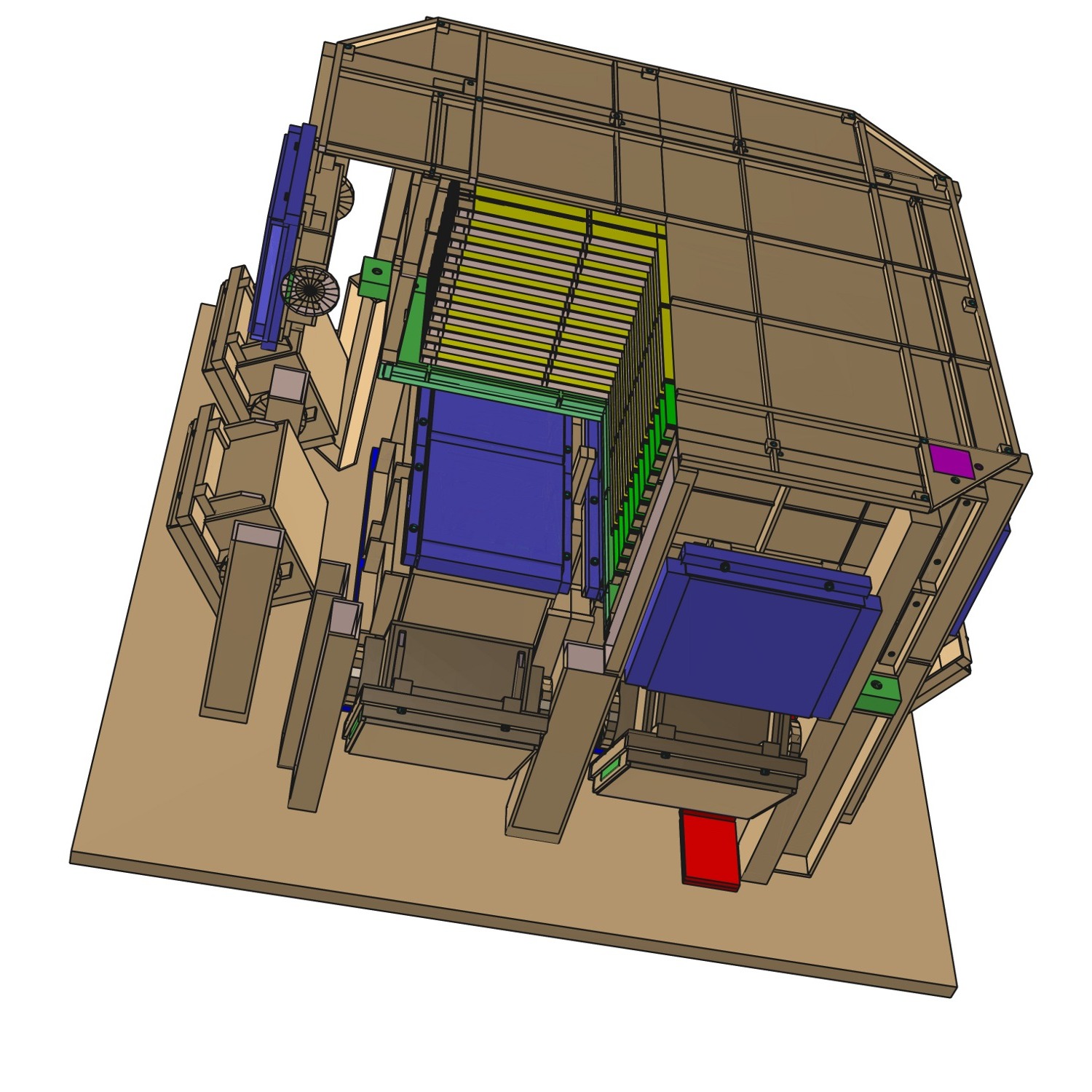
Geomega is one of the central tools of MEGAlib as it provides the geometry and detector description for all other tools. The picture shows the geometry model of the MEGA prototype detector as modeled with Geomega and displayed with ROOT's openGL viewer.
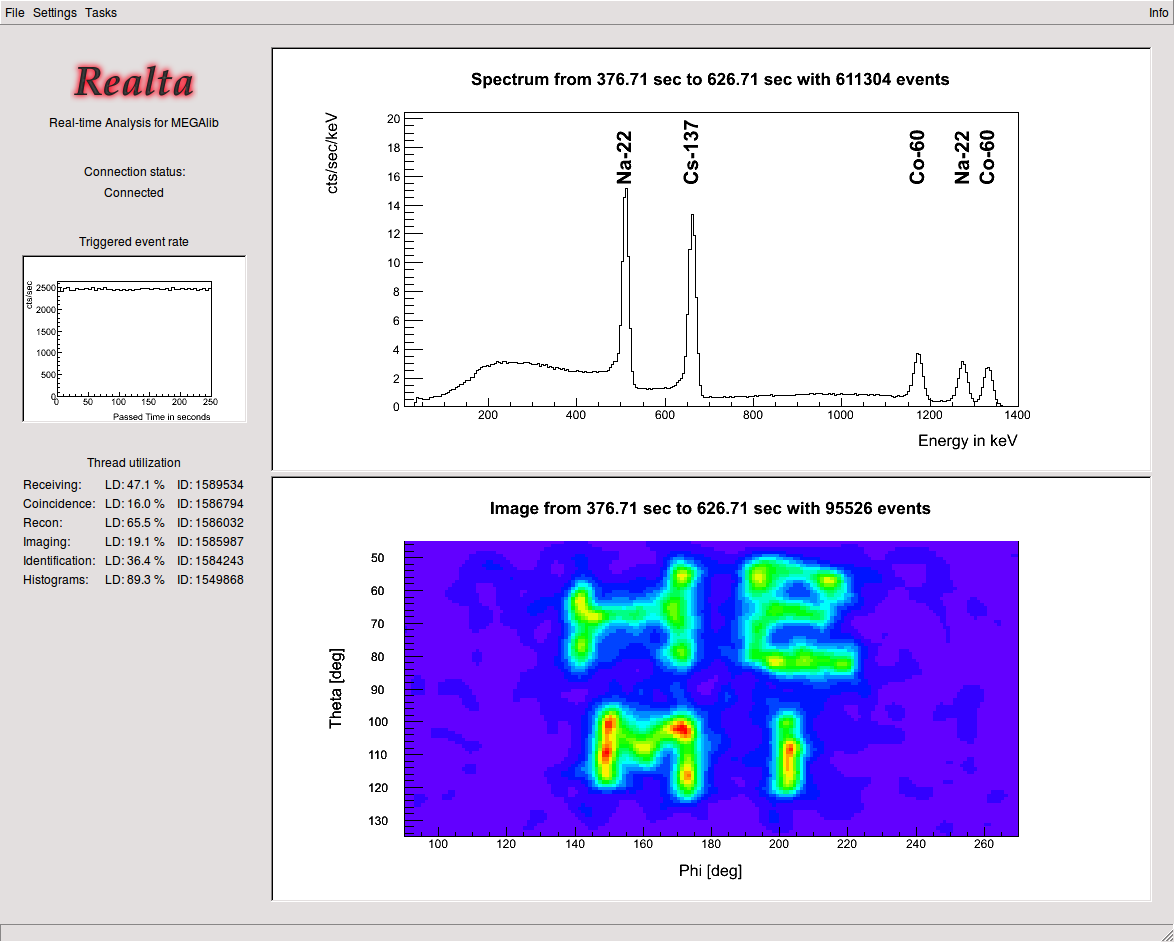
MEGAlib's Realta tool provides real-time analysis for Compton telescopes. The image shows its user interface, with a real-time updated spectrum on the top with automatic isotope identification, and real-time Compton imaging in the bottom window. In this example an extended source displaying the word HEMI is reconstructed - the name of the detector which measured the data.
It all began on a cold, dark November evening. I just spend the last days to get SuSE 5.3 up and running on my brand new computer - a Pentium II with 233 MHz, 32 MB RAM and a 4 GB hard drive! In the early days of Linux, and in the pre-google and pre-internet-at-home era it wasn't always easy. But I was successful, and I just had to install that fancy new object-oriented data analysis library from CERN, ROOT . And then I was ready to start my brand new undergrad project. I wrote:
Int_t main(Int_t argc, Char_t** argv)
It was November 20, 1998 - the day when MEGAlib was born!
MEGAlib
The Medium-Energy Gamma-ray Astronomy library, MEGAlib, is a set of software tools which are designed to simulate and analyze data of gamma-ray detectors, with a specialization on Compton telescopes. While MEGAlib was originally developed for astrophysics, it has been expanded and used for ground based applications such as medical imaging and environmental monitoring. The library comprises all necessary data analysis steps from simulation/measurements via calibrations and event reconstruction to high-level data analysis such as image reconstruction.
MEGAlib contains a geometry and detector description tool for the detailed modeling of different detector types and characteristics, and provides an easy to use simulation program based on Geant4 . For different Compton telescope detector types (electron tracking, multiple Compton or time of flight based) specialized Compton event reconstruction algorithms are implemented in different approaches (Chi-square and Bayesian). The high level data analysis tools allow to calculate response matrices, perform image deconvolution (specialized in list-mode-likelihood-based Compton image reconstruction), determine detector resolutions and sensitivities, retrieve spectra, determine polarization modulations, etc.
The highly modular and completely object-oriented library is written in C++ and utilizes ROOT and Geant4 . While it has been originally developed for the Compton scattering and pair creation telescope MEGA, it also has been successfully applied to a wide variety of hard X-ray/gamma-ray telescopes in space and on ground. MEGAlib is currently the main data analysis framework for COSI , but has also been used for AMEGO , COMPTEL , ACT , NuSTAR , GRI , GRIPS , HEMI, and many more
For a general overview of MEGAlib consider reading MEGAlib's key reference Andreas Zoglauer et al., "MEGAlib - Medium Energy Gamma-ray Astronomy Library", NewAR 50 (7-8), 2006 .